While the economy has stabilized in some regards, architects are still suffering.
Just when it seemed that the architecture industry might be pulling out of its tailspin, some key economic indicators are suggesting that a recovery might take longer than expected.
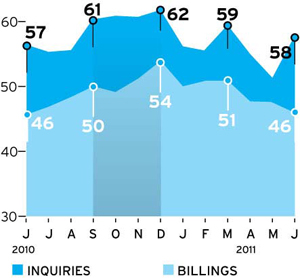
The Architecture Billings Index, a measure of the industry’s health compiled by the American Institute of Architects, has dipped below 50 for three consecutive months, posting scores of 47.6 (April), 47.2 (May), and 46.3 (June). Those dips came after five straight months of the ABI hovering at or above 50, a sign of increased activity.
Moreover, Engineering News-Record’s Construction Industry Confidence Index—based on surveys sent to contractors, subcontractors, engineers and architects—fell five points in the second quarter of 2011, from 51 to 46.
That data doesn’t surprise architect Charles Dalluge of the Omaha-based firm Leo A. Daly, which has 31 offices around the world. Even though some architects were publicly predicting that “it would be heaven in 2011,” he says, a lot of firms are still suffering.
And he might know. In June, his firm laid off 50 employees from various offices, including architects and engineers. Dalluge defends the move as part of a “strategic repositioning” that will result in the hiring of 50 workers with specialties in areas of growth, such as healthcare. The firm now has 900 employees.
But even a healthcare focus may not be enough to keep some firms alive. In June, Karlsberger, a Columbus, Ohio-based healthcare-focused firm, closed after 83 years in business. None of the firm’s managers would comment on the shuttering, which is believed to have resulted in 40 job cuts. A statement on its website, however, blamed the state of the market for its woes. “Our level of revenues are insufficient for us to meet our ongoing obligations,” it says.
Karlsberger’s former president, Mitchel Levitt, who resigned in April 2010 after 31 years, told RECORD that the firm lost a major lawsuit that made it difficult to go on. The suit was brought against Ohio State University, one of Karlsberger’s largest clients, over the school’s termination of a contract for a $1 billion medical center expansion; the lawsuit was dismissed in December. “It probably hurt them,” Levitt said in an interview conducted in June. “But I thought they had done what they needed to do to continue to operate.”
While the new office building market may show few signs of turnaround, especially while jobs are scarce, a bright spot appears to be college work. Many schools’ endowments were wiped out in the recession but are now being replenished by a robust stock market, which means that many stalled university projects are back on track.
Indeed, the economic downturn suspended a renovation of Yale’s 1928 Swartwout Building, designed by Egerton Swartout. But that project recently resumed, says Richard Olcott, partner at New York-based Ennead Architects, which is overseeing the renovation. Olcott adds that his firm didn’t lay off any workers during the recession; in fact, it hired 40 people in the last year, including architects, for a grand total of 160 employees.
Even public universities, once hurt by dwindling tax-collection revenues, are restarting projects, according to Ayers Saint Gross, a Baltimore design firm at work on a once-stalled science building for the University of Delaware.
The firm added 18 people last year and is now looking to hire five more, including architects. It now has 130 employees, its highest-ever headcount, said Adam Gross, a principal. “I think the indicators are pretty serious,” he said, referring to the ABI and other worrisome data, “but not as serious as we experienced” in the fall of 2008.

Post a comment to this article
Report Abusive Comment